Feature Coming Soon!
The newsletter functionality is under development.
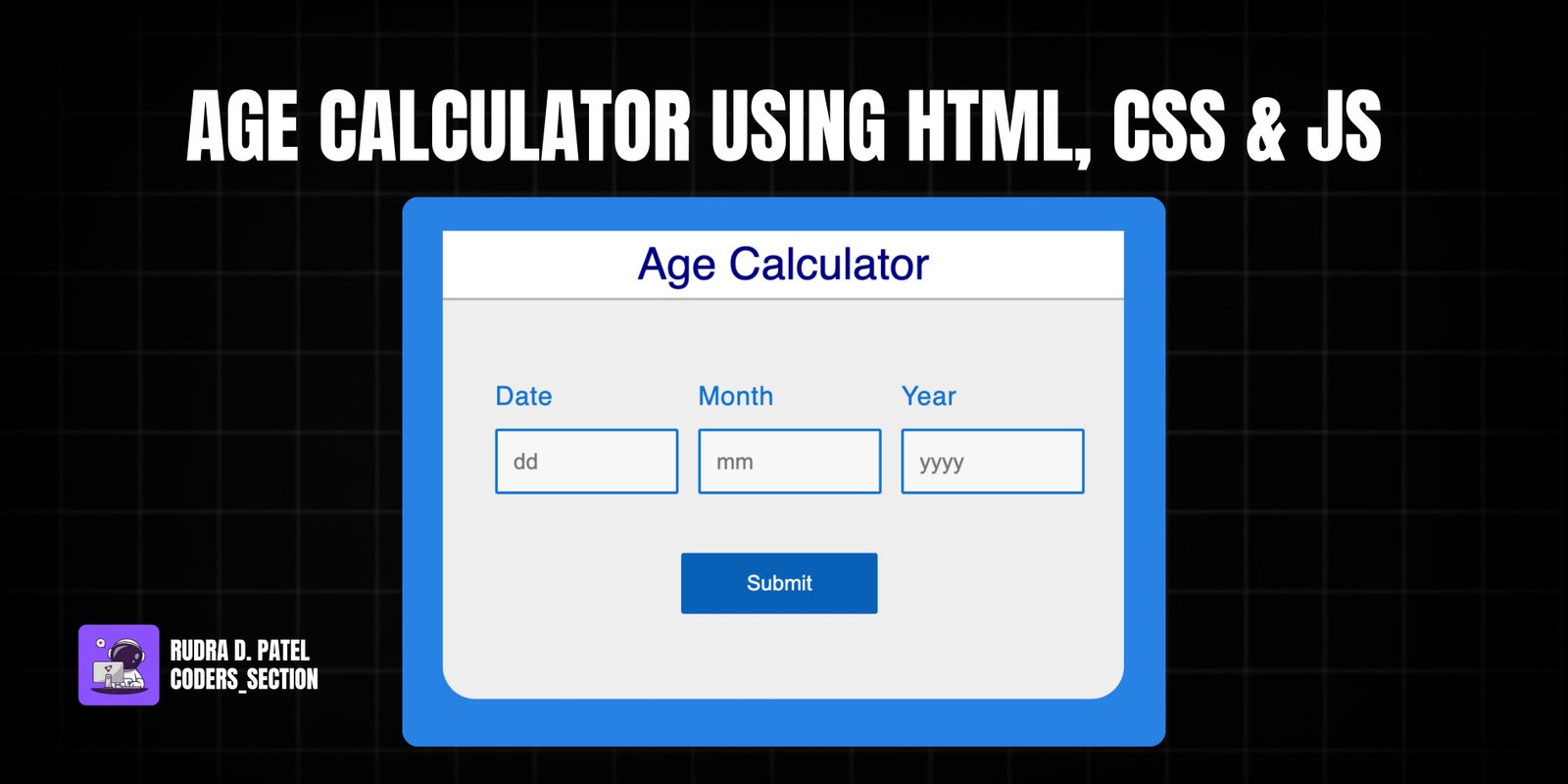
This project features a simple yet effective Age Calculator, built using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It allows users to input their birth date, month, and year, and then calculates their exact age in years, months, and days based on the current date. This tool is designed for ease of use, providing a clear and precise age calculation with a straightforward interface.
Key functionalities include input fields for day, month, and year, along with a "Submit" button to trigger the calculation. The JavaScript handles the date parsing, performs the age calculation by considering leap years and varying month lengths, and displays the result in a user-friendly format. The design is clean and minimal, focusing on functionality and readability, making it a practical example for basic web development and date manipulation in JavaScript.
The HTML structure for the Age Calculator is straightforward, centered around a `form` element within a `container` `div`. It includes three `input` fields for the user to enter their birth date, month, and year, each wrapped in a `block` `div` with a `title` paragraph. A "Submit" button is provided to trigger the age calculation, which calls the `age()` JavaScript function on click. Finally, a `div` with the ID `age` is designated to display the calculated age. This clean HTML provides a clear and intuitive interface for the user to interact with the calculator.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" >
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Age Calculator | Coders_Section</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<!-- partial:index.partial.html -->
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="base">
<div class="enter">
<h4>Age Calculator</h4>
</div>
<div class="block">
<p class="title">Date</p>
<input type="text" name="date" id="date" placeholder="dd" required="required" minlength="1"
maxlength="2" />
</div>
<div class="block">
<p class="title">Month</p>
<input type="text" name="month" id="month" placeholder="mm" required="required" minlength="1"
maxlength="2" />
</div>
<div class="block">
<p class="title">Year</p>
<input type="text" name="year" id="year" placeholder="yyyy" required="required" minlength="4"
maxlength="4" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="base">
<div class="enter">
<input type="button" name="submit" value="Submit" onclick="age()" />
</div>
</div>
<div id="age"></div>
</form>
</div>
<!-- partial -->
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
The CSS for the Age Calculator is designed to provide a clean, centered, and user-friendly interface. It sets a background color for the `body` and centers the main `container` for the calculator. The `.base` and `.block` classes are used for layout, ensuring inputs are neatly arranged. Titles for date, month, and year inputs are styled for readability. Input fields are given a consistent appearance with borders, padding, and focus states. The "Submit" button is styled with a distinct background color and hover effect. The `#age` div, where the result is displayed, is formatted with a clear font size and color, ensuring the calculated age is easily visible to the user.
body {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
background-color: #2782e3;
font-size: 15px;
line-height: 1.5;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.container {
width: 520px;
height: auto;
margin: 100px auto;
background-color: #eee;
border-radius: 25px;
}
.base {
width: 100%;
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
display: block;
float: none;
}
.block {
width: 135px;
padding: 5px 20px;
margin-left: 20px;
display: inline-block;
float: left;
}
.base h4 {
font-size: 26px;
text-align: center;
font-family: sans-serif;
font-weight: normal;
margin-top: 0px;
box-shadow: 0px 2px #bababa;
background: white;
font-size: 34px;
color: navy;
}
.title {
font-size: 20px;
text-align: left;
font-family: sans-serif;
font-weight: normal;
line-height: 0.5;
letter-spacing: 0.5px;
word-spacing: 2.7px;
color: #1073d0;
}
input[type="text"] {
width: 140px;
margin: auto;
outline: none;
min-height: 50px;
border: 2px solid #1073d0;
padding: 12px;
background-color: #f7f7f7;
border-radius: 2px;
color: #1073d0;
font-size: 17px;
}
input[type="text"]:focus {
background-color: #ffffff;
border: 2px solid orange;
outline: none;
}
input[type="button"] {
width: 150px;
margin-left: 35%;
margin-top: 40px;
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 2px;
background-color: #0761b6;
color: #ffffff;
padding: 14px 16px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 16px;
}
input[type="button"]:hover {
background-color: #003669;
}
#age {
display: block;
margin: 10px;
margin-top: 35px;
padding: 10px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
overflow: hidden;
font-family: verdana;
font-size: 23px;
font-weight: normal;
line-height: 1.5;
word-spacing: 2.7px;
color: navy;
}
The JavaScript for the Age Calculator is responsible for performing the core age calculation logic. The `age()` function is triggered when the "Submit" button is clicked. It retrieves the user's input for date, month, and year. It then gets the current date, month, and year. The script includes logic to handle scenarios where the birth day is greater than the current day (by borrowing days from the previous month) and where the birth month is greater than the current month (by borrowing months from the previous year). Finally, it calculates the difference in days, months, and years, and updates the inner HTML of the `age` `div` to display the calculated age in a readable format.
function age() {
var d1 = document.getElementById("date").value;
var m1 = document.getElementById("month").value;
var y1 = document.getElementById("year").value;
var date = new Date();
var d2 = date.getDate();
console.log(d2)
var m2 = 1 + date.getMonth();
var y2 = date.getFullYear();
var month = [31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31];
if (d1 > d2) {
d2 = d2 + month[m2 - 1];
m2 = m2 - 1;
}
if (m1 > m2) {
m2 = m2 + 12;
y2 = y2 - 1;
}
var d = d2 - d1;
var m = m2 - m1;
var y = y2 - y1;
document.getElementById("age").innerHTML =
"Your Age is " + y + " Years " + m + " Months " + d + " Days";
}
Watch a live demonstration of the Age Calculator below.
This Age Calculator project provides a practical and accessible tool for quickly determining one's age. It serves as an excellent foundational example for understanding basic HTML form handling, CSS styling, and JavaScript date manipulation. The clear separation of concerns between structure, style, and logic makes it easy to understand and modify.
You can easily customize this component by:
For more robust date handling and calculations, consider using a dedicated JavaScript date library like Moment.js or date-fns. These libraries provide powerful and convenient functions for parsing, formatting, and manipulating dates, simplifying complex date-related logic.
Click the button below to download the full source code. Download will be ready in 10 seconds.
Receive coding tips and resources updates. No spam.
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe at any time.